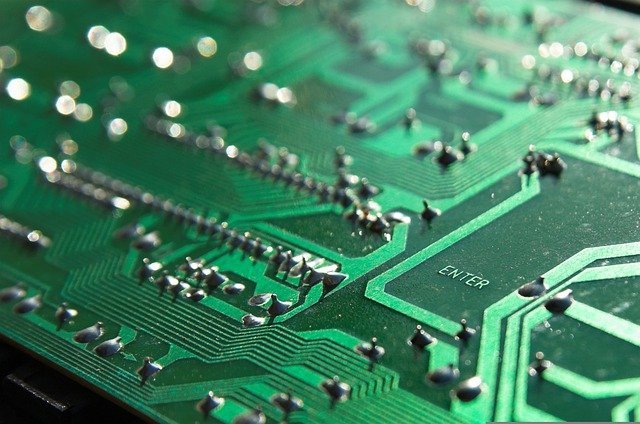
A printed circuit board, or PCB, is a thin board made of non-conductive material that is used to support and connect electronic components. The most common type of PCB is the FR4, which is made of glass-reinforced epoxy laminate.
PCBs are found in a variety of electronic devices, from computers and cell phones to televisions and home appliances. They are used to connect and support the electronic components that make up these devices.
Printed circuit boards are made up of a number of different layers.
The substrate is the bottom layer, which is made of either FR4 or CEM-3. This layer provides support for the other layers.
The next layer is the copper foil, which is bonded to the substrate using an adhesive. The copper foil conducts electricity and connects the different components on the PCB.
How are printed circuit boards made?
A printed circuit board, or PCB, is a self-contained module of interconnected electronic components found in devices ranging from common beepers, pagers, and radios to sophisticated radar and computer systems.
The circuits are formed by a thin layer of conducting material deposited, or “printed,” on the surface of an insulating board known as the substrate.
PCBs can be single-sided (one copper layer), double-sided (two copper layers on both sides of the substrate), or multi-layered (outer and inner layers of copper interconnecting through vias).
Etching removes unwanted copper from the board to leave only the desired traces or patterns.
The boards are then drilled so that component leads can be inserted and soldered into place.
A solder mask, a lacquer-like material, is applied to protect the exposed copper circuitry from oxidation and short circuits.
The benefits of printed circuit boards
Printed circuit boards, or PCBs, are used in nearly every type of electronic device. They are found in everything from televisions and radios to computers and cell phones. A PCB is made up of a thin piece of insulating material, typically fiberglass, with conductive pathways etched onto it. These pathways connect the various components of the device together.
PCBs have several advantages over other methods of electrical connection:
- They are much smaller and take up less space than point-to-point wiring. This allows for smaller devices and more compact packaging.
- Because the components are all connected by etched pathways, no loose wires can come loose and cause shorts or other problems.
- PCBs can be mass-produced very cheaply compared to other methods of electrical connection.
The challenges of printed circuit boards
Printed circuit boards, or PCBs, are one of the most important components of modern electronics. They are used in everything from computers to cell phones to TVs. But designing and manufacturing PCBs is not easy. Many challenges need to be overcome.
One challenge is creating circuits that are small enough to fit onto a PCB. As electronic devices get smaller and smaller, the circuits need to be even tinier. This presents a big challenge for designers and manufacturers.
Another challenge is making sure that the circuit works correctly. With such tiny components, it is easy for something to go wrong during the manufacturing process. This can cause serious problems down the line.
Finally, cost is always a factor in manufacturing PCBs. Because they are so complex, they can be quite expensive to produce.
Various applications of printed circuit boards
PCBs are used in a wide variety of electronic applications, including:
- Computers: PCBs connect and support various components, such as the CPU, RAM, motherboard, and peripherals.
- Smartphones: PCBs connect and support various components, such as the processor, memory, display, and camera.
- Appliances: PCBs are used in appliances to control and power various components, such as motors, heating elements, and displays.
- Industrial equipment: PCBs control and power various components, such as motors, sensors, and displays.
- Automotive: PCBs are used in automotive applications to control and power various components, such as engines, transmissions, and displays.
- Medical devices: PCBs connect and support various components, such as sensors, displays, and control systems.
- Military: PCBs are used in military applications to connect and support various components, such as sensors, communications systems, and control systems.
- Aerospace: PCBs are used in aerospace applications to connect and support various components, such as sensors, communications systems, and control systems.
In each of these applications, PCBs provide a reliable and cost-effective way to electrically connect and mechanically support the various components, allowing for the creation of complex electronic systems.