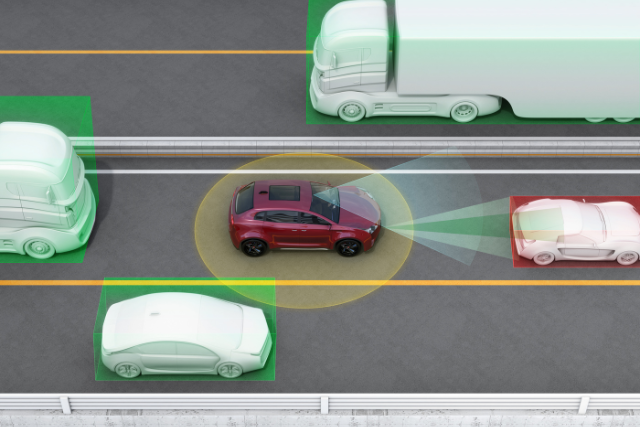
Electronic Control Units (ECUs) are pivotal components in contemporary automobiles, responsible for managing many electronic systems that enhance vehicle performance, safety, and efficiency.
This article focuses on the basics of ECUs, their functions, types, and the technological advancements propelling the automotive industry forward.
Understanding the Basics of an ECU
An Electronic Control Unit (ECU) is a microcontroller-based system that manages electronic components of vehicles. ECUs collect data from various sensors dispersed throughout the car, process this information, and issue commands to actuators to execute specific functions.
This automated process optimizes vehicle performance, improves fuel efficiency, and enhances safety features.
Functions of an ECU
ECUs serve several critical functions in a vehicle, including:
Engine Control: Manages fuel injection, ignition timing, and air-fuel ratios to optimize engine performance and efficiency.
Transmission Control: Adjusts gear shifts for smooth operation and improved fuel economy.
Braking System Control: Oversees anti-lock braking systems (ABS) to prevent wheel lockup during braking.
Stability Control: Enhances vehicle stability by managing traction control systems.
Climate Control: Regulates air conditioning and heating systems for passenger comfort.
Types of ECUs in Modern Vehicles
Modern vehicles feature numerous ECUs, each tailored to control specific functions. The number of ECUs varies based on the vehicle’s complexity and features. Key types include:
Engine Control Module (ECM): Manages all aspects of engine operation, including fuel injection, ignition timing, and emissions control.
Transmission Control Module (TCM): Controls the transmission system, ensuring smooth gear shifts and optimizing performance.
Body Control Module (BCM): Oversees body-related functions such as lighting, power windows, central locking, and windshield wipers.
ABS Control Module: Ensures wheels do not lock up during braking, providing better control and preventing skidding.
Airbag Control Module: Manages the deployment of airbags during collisions to protect passengers.
Climate Control Module: Regulates the HVAC system to maintain a comfortable cabin environment.
Infotainment Control Module: Manages multimedia systems, including audio, navigation, and connectivity features.
How Do ECUs Work?
The operation of an ECU can be broken down into three primary steps: input, processing, and output.
Input: ECUs receive data from sensors located throughout the vehicle. These sensors monitor engine speed, temperature, air-fuel ratio, and wheel speed.
Processing: The ECU’s microcontroller processes the input data using pre-programmed algorithms. Decisions are made based on this data to optimize vehicle performance and safety.
Output: After processing the data, the ECU sends commands to actuators to perform specific actions, such as adjusting the throttle position or activating fuel injectors.
Technological Advancements in ECUs
Advancements in technology have made ECUs more sophisticated, enabling them to manage complex vehicle systems. Key trends include:
Integration and Miniaturization: Combining multiple functions into a single ECU to reduce complexity and weight.
Enhanced Processing Power: Increased microcontroller capabilities allow more complex algorithms and real-time data processing.
Connectivity and Communication: Advanced communication protocols like CAN (Controller Area Network), LIN (Local Interconnect Network), and FlexRay facilitate seamless integration.
Software Updates: Over-the-air (OTA) updates enable software improvements without requiring a service centre visit.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: AI and machine learning integration allow for predictive maintenance, adaptive cruise control, and autonomous driving features.

Benefits of ECUs in Automobiles
The implementation of ECUs in vehicles brings numerous advantages that significantly enhance performance and safety:
Improved Fuel Efficiency:
- Optimal Air-Fuel Ratio: ECUs adjust the air-fuel mixture to maintain the ideal ratio, crucial for combustion efficiency. This improves fuel economy and reduces harmful emissions.
- Adaptive Learning: Modern ECUs continuously use adaptive learning algorithms to improve fuel efficiency based on driving habits and conditions.
- Reduced Idle Fuel Consumption: ECUs manage the engine’s idle speed to minimize fuel consumption when the vehicle is stationary.
Enhanced Safety Features:
- Anti-lock Braking System (ABS): ECUs control ABS to prevent wheel lockup during sudden braking, maintaining vehicle control and reducing stopping distances on slippery surfaces.
- Electronic Stability Control (ESC): By monitoring vehicle dynamics, ECUs can prevent skidding or loss of control, enhancing driver safety during cornering or evasive manoeuvres.
- Airbag Deployment: ECUs govern the deployment of airbags based on sensor data from crash detection systems, ensuring timely and effective protection for occupants during collisions.
- Adaptive Cruise Control: This system uses ECU-controlled sensors to maintain a safe distance from the vehicle ahead, adjusting speed as necessary to prevent collisions.
Better Vehicle Performance:
- Smooth Gear Shifts: Transmission Control Modules (TCMs) manage gear shifts for seamless transitions, improving performance and comfort.
- Enhanced Acceleration: By optimizing engine and transmission parameters, ECUs can enhance acceleration response, providing better power delivery when needed.
- Precise Throttle Control: ECUs regulate the throttle position for smoother and more responsive acceleration.
- Dynamic Handling: Stability control systems managed by ECUs adjust braking and engine power to improve vehicle handling during challenging driving conditions.
Increased Reliability:
- Early Issue Detection: ECUs can detect potential problems before they become serious, allowing for timely maintenance and repairs.
- Error Logging: When an issue is detected, ECUs log error codes that can be read by diagnostic tools, facilitating quick and accurate repairs by technicians.
- Component Protection: By managing various vehicle systems, ECUs help protect critical components from damage due to incorrect operation or environmental factors.
Customization and Adaptability:
- Performance Tuning: ECUs can be programmed to adjust engine parameters for different driving modes, such as eco, sport, or off-road.
- Software Updates: Over-the-air (OTA) updates enable manufacturers to remotely deliver new features, enhancements, and bug fixes.
- Adaptive Systems: ECUs support adaptive systems that adjust to changing conditions, such as adaptive lighting that alters headlight intensity based on ambient light and speed.
- Personalized Settings: Drivers can customize various vehicle settings, from climate control preferences to infotainment system configurations.

Challenges of ECUs
While ECUs bring significant benefits, they also pose several challenges and present opportunities for future advancements:
Complexity and Integration:
- Interoperability: Ensuring that all ECUs, often from different manufacturers, work together without conflict requires standardized communication protocols.
- System Architecture: Developing a cohesive system architecture that integrates numerous ECUs efficiently while minimizing latency and maximizing reliability.
- Maintenance and Troubleshooting: Diagnosing and resolving issues in a highly integrated system can be complicated, requiring sophisticated diagnostic tools and expert knowledge.
Cybersecurity:
As vehicles become increasingly connected, they become more susceptible to cyber-attacks. Ensuring the cybersecurity of ECUs is paramount to protect against unauthorized access and control:
- Data Protection: Securing sensitive data transmitted between ECUs and external systems to prevent interception and tampering.
- Access Control: Implementing robust authentication mechanisms ensures only authorized users and systems can access ECU functionalities.
- Vulnerability Management: Continuously monitoring for and addressing vulnerabilities in ECU software to prevent exploitation by malicious actors.
Cost:
The development and integration of advanced ECUs come with significant costs:
- High-Performance Components: Advanced ECUs require powerful microcontrollers, sensors, and actuators.
- Research and Development: Extensive R&D efforts are necessary to design, test, and validate ECUs.
- Manufacturing and Quality Control: Producing high-quality ECUs with rigorous quality control measures is essential to ensure reliability and durability.
Future Trends
The future of ECUs is poised for significant evolution, driven by advancements in technology and the changing landscape of the automotive industry:
- Further Integration and Miniaturization: Future ECUs will likely integrate multiple functions into a single unit to reduce complexity, weight, and space requirements.
- Increased Processing Power: Advancements in microcontroller technology will lead to ECUs with more outstanding processing capabilities, enabling more complex algorithms and real-time data processing.
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: AI and machine learning will enable ECUs to learn from data, improve decision-making, and enhance vehicle performance and safety.
- Autonomous Driving: ECUs will be crucial in developing autonomous vehicles and managing complex tasks such as sensor fusion, path planning, and real-time decision-making.
- Predictive Maintenance: ECUs equipped with AI capabilities will monitor vehicle health and predict potential failures before they occur, reducing downtime and maintenance costs.
Learn More: Future Trends in Vehicle Safety
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is an ECU in an automobile?
An ECU (Electronic Control Unit) is a microcontroller-based system that manages various electronic functions in vehicles, optimizing performance, safety, and efficiency.
How many ECUs are typically found in a modern vehicle?
The number of ECUs varies widely, with some vehicles having up to 100 ECUs, each managing different functions such as engine control, transmission, braking, and infotainment.
What is the role of the Engine Control Module (ECM)?
The ECM is a critical ECU that manages engine performance, including fuel injection, ignition timing, and emissions control, ensuring efficient operation and regulatory compliance.
How do ECUs communicate with each other?
ECUs communicate using protocols such as CAN (Controller Area Network), LIN (Local Interconnect Network), and FlexRay, enabling seamless data exchange and coordination between vehicle systems.
Can ECUs be updated?
Modern ECUs can receive over-the-air (OTA) software updates, allowing manufacturers to fix bugs, update software, and introduce new features without requiring a service center visit.
What are the challenges associated with ECUs in vehicles?
Challenges include the complexity of integrating multiple ECUs, cybersecurity risks, and balancing cost with performance and reliability. Ensuring seamless communication and protecting against cyber-attacks are critical.
Conclusion
Electronic Control Units (ECUs) are the backbone of modern automotive technology, ensuring vehicles operate efficiently, safely, and smoothly.
ECUs continue to evolve, integrating more functions and adopting new capabilities such as AI and machine learning. The future of ECUs promises even more significant advancements in vehicle performance, safety, and connectivity.