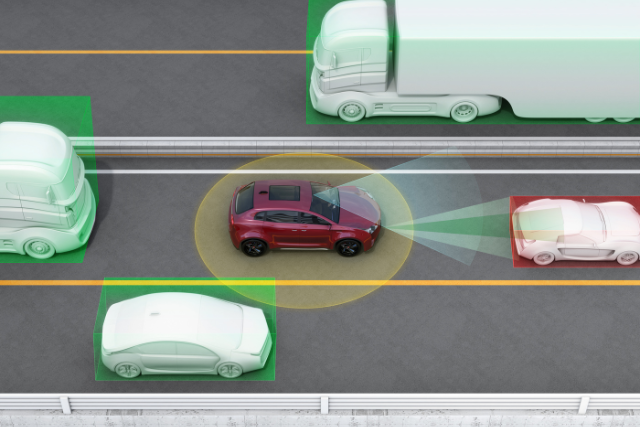
Do you ever wonder how your car’s antilock braking system (ABS) works?
In this article, we’ll take you through the basics of ABS, the key components involved, and how it detects wheel locking.
We’ll also discuss how ABS controls and modulates the braking process.
The Basics of ABS
ABS, or Antilock Braking System, is a safety feature that prevents the wheels from locking up during braking.
Its main function is to maintain traction between the tires and the road surface, allowing the driver to maintain control of the vehicle.
ABS is particularly effective in emergency braking situations, where sudden stops may be necessary to avoid a collision.
This safety feature has become a standard in most modern vehicles, providing enhanced stability and control during braking manoeuvres.
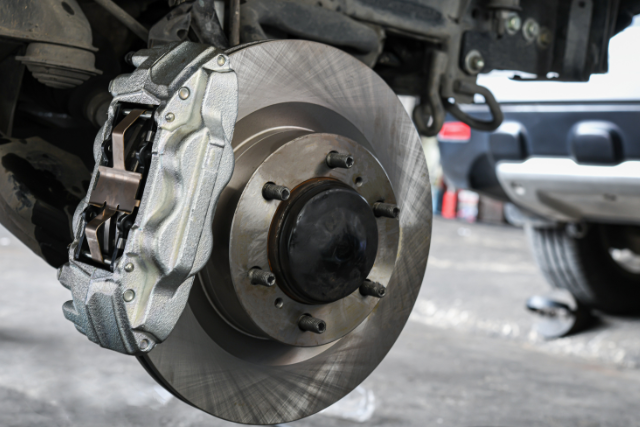
Components of an ABS
The main components of an Antilock Braking System include the speed sensors, the hydraulic control unit (HCU), the electronic control unit (ECU), and the brake modulator.
The speed sensors are responsible for measuring the rotational speed of each wheel. They provide crucial input to the ECU, which analyzes the data and determines whether wheel lockup is imminent.
The HCU is responsible for controlling the hydraulic pressure of each brake. It receives signals from the ECU and adjusts the pressure accordingly.
The brake modulator is the component that applies and releases the brake pressure to prevent wheel lockup.
Together, these components work in harmony to ensure optimal braking performance and prevent wheel lockup during emergency braking situations.
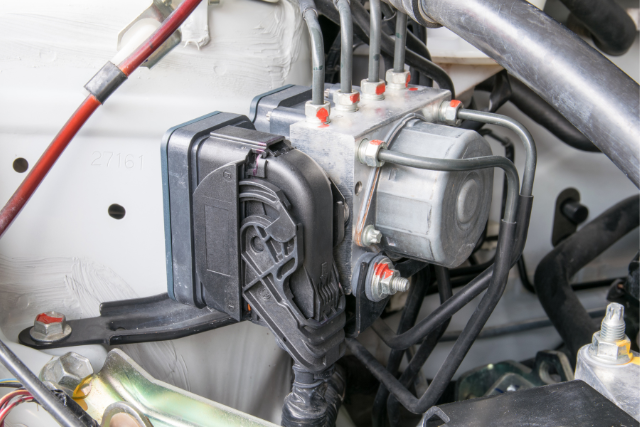
How ABS Detects Wheel Locking
To detect wheel locking, an ABS utilizes speed sensors to measure the rotational speed of each wheel. These sensors are typically located on the wheel hub or inside the transmission.
As you apply the brakes, the ABS continuously monitors the wheel speeds. If one or more wheels are on the verge of locking up, the ABS will detect a significant decrease in rotational speed compared to the others. This indicates that the wheel is about to stop rotating, leading to potential skidding and loss of control.
Once the ABS detects wheel locking, it intervenes by modulating the brake pressure to that particular wheel. It does this by rapidly and repeatedly applying and releasing the brakes, allowing the wheel to rotate without locking up.
ABS Control and Modulation
The ABS control and modulation are responsible for applying and releasing the brakes rapidly to prevent wheel lock-up during braking. When you apply the brakes, the ABS control module monitors the wheel speed sensors to detect any wheel lock-up.
If a wheel is about to lock up, the ABS control module reduces the brake pressure on that wheel by modulating the hydraulic pressure. By rapidly applying and releasing the brakes, the ABS allows the wheels to maintain traction with the road surface, ensuring you have steering control while braking.
This modulation process happens multiple times per second, allowing you to maintain control of your vehicle even in emergency braking situations.
Benefits and Limitations of ABS
ABS offers several key benefits that enhance vehicle safety.
- It prevents wheel lock-up during braking, ensuring that you maintain control and stability. This is especially important on slippery surfaces or in emergencies requiring sudden stops.
- ABS allows you to steer while braking, increasing your ability to avoid obstacles and potential collisions.
- ABS reduces braking distance, enabling you to stop more quickly and potentially prevent accidents.
However, ABS does have some limitations.
- It may increase stopping distances on loose or uneven surfaces and may be less effective in certain weather conditions, such as deep snow or ice.
- ABS can’t overcome the laws of physics and can’t compensate for worn-out or improperly maintained brakes.
Despite these limitations, ABS remains a crucial safety feature in modern vehicles.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can ABS Prevent All Accidents?
No, ABS can’t prevent all accidents. While it helps improve braking control and stability during emergencies, it doesn’t guarantee accident prevention.
It’s important always to drive safely and remain alert on the road.
What Are the Common Maintenance Issues With Abs?
The common maintenance issues with ABS include:
- Sensor malfunctions
- Faulty wiring
- Hydraulic system leaks
Regular inspections and maintenance can help identify and address these issues, ensuring the proper functioning of your ABS.
How Does ABS Interact With Other Safety Systems in a Vehicle?
ABS, or Anti-lock Braking System, is a safety feature designed to prevent a vehicle’s wheels from locking up during braking. By automatically modulating the brake pressure on each wheel, ABS helps to maintain traction and control, especially in emergencies.
This allows the driver to maintain steering control while braking hard, reducing the risk of skidding or losing vehicle control. ABS works with other safety systems in your vehicle, such as traction control and electronic stability control, to enhance overall safety.
By preventing wheel lock-up, ABS helps reduce the stopping distance and improve the vehicle’s stability during braking. It is important to note that ABS does not guarantee that the vehicle will stop in a shorter distance, but it does help to provide better control and stability while braking.
Can ABS Be Retrofitted Into Older Vehicles?
Yes, ABS can be retrofitted into older vehicles.
It’s a worthwhile investment as it improves braking efficiency and safety.
Consult a professional mechanic to determine compatibility and to ensure proper installation.
Are There Any Situations Where ABS Can Hinder Braking Performance?
In some situations, ABS can hinder braking performance.
For example, on loose or slippery surfaces, ABS may cause the wheels to lock up and decrease the stopping distance.
Conclusion
So, now you know how the antilock braking system (ABS) works.
ABS is a crucial safety feature in modern vehicles that prevents wheel lock-up during braking, allowing for improved steering control.
By detecting wheel locking and modulating brake pressure, ABS ensures a shorter stopping distance and better vehicle stability.
Although ABS has limitations, it undoubtedly plays a vital role in enhancing road safety and preventing accidents.